Edited by Aditya Karhade and Brian Goh - 7/1/2021
Inspection/Palpation
- Global coronal (scoliosis) and sagittal (kyphosis, lordosis) alignment assessed while standing
- Prior incisions
- Step-offs, palpable deformity
Neurovascular Exam
Gait Have the patient ambulate if able which can demonstrate strength and balance
Neurologic compromise can be classified via the ASIA scale.
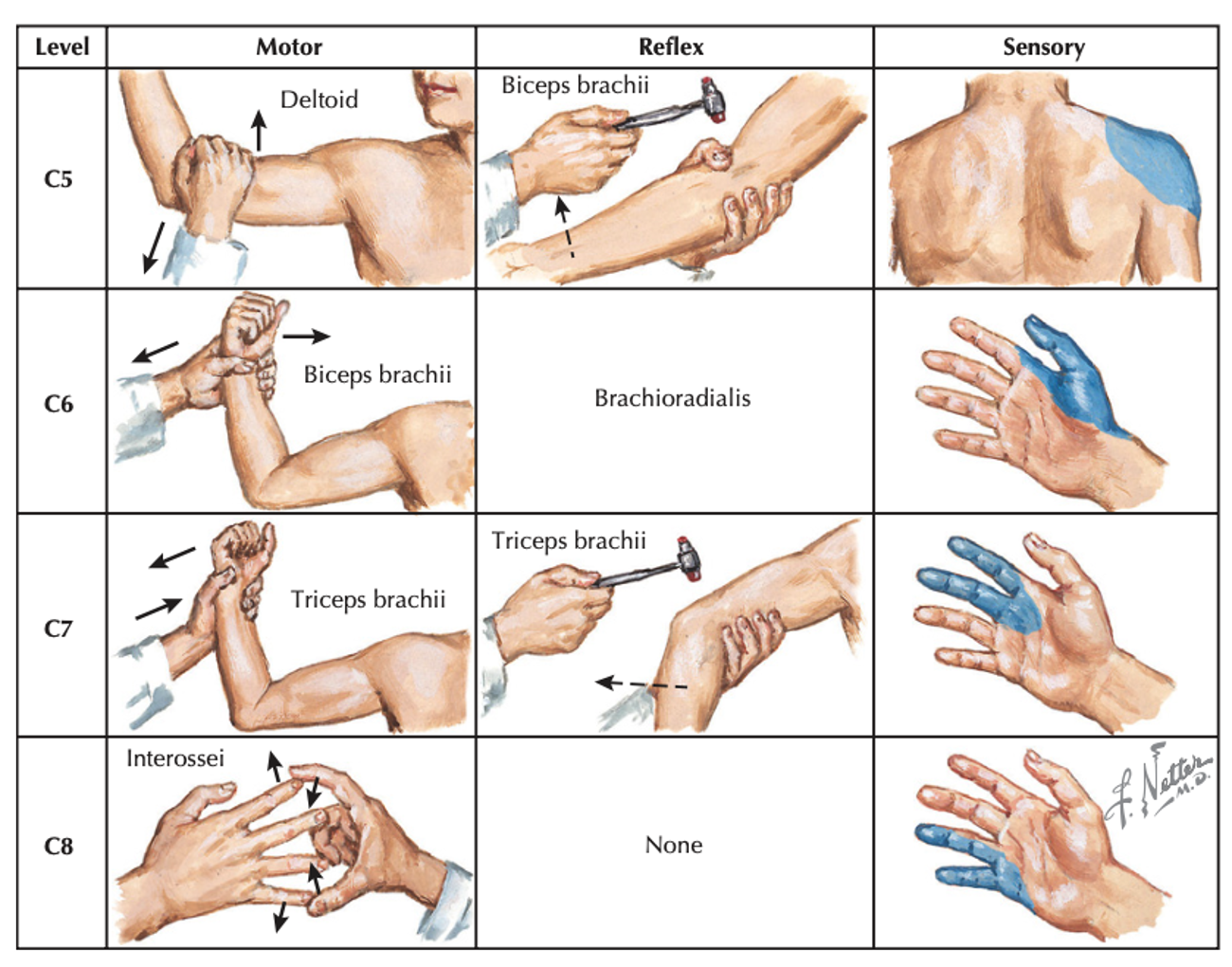
Upper extremity
Motor
- C5: elbow flexors
- C6: wrist extensors
- C7: elbow extensors
- C8: finger flexors
- T1: finger abductors
Sensory
- C5: lateral deltoid
- C6: thumb
- C7: long finger
- C8: small finger
- T1: medial epicondyle
Lower extremity
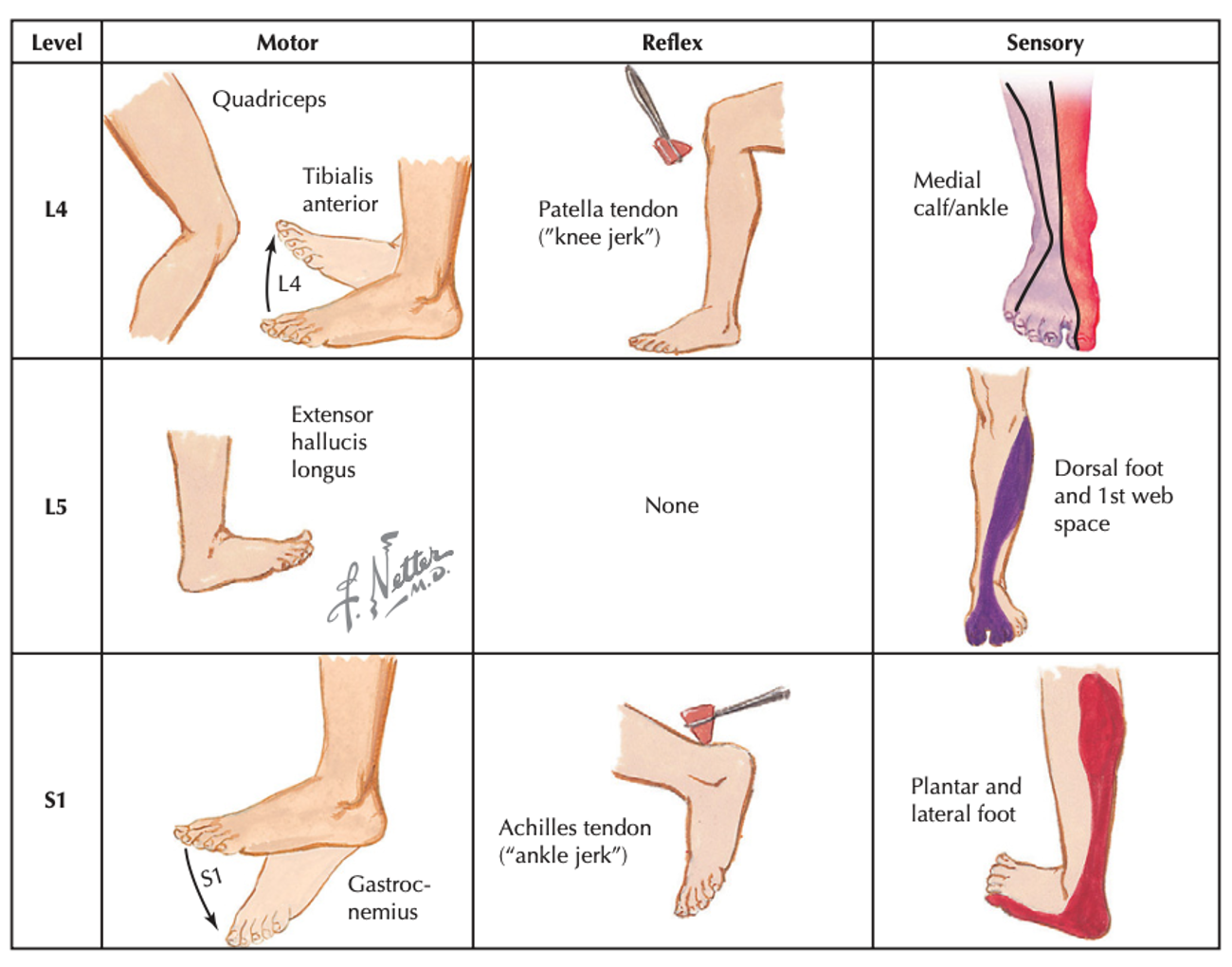
Motor
- L2: hip flexors
- L3: knee extension
- L4: ankle dorsiflexion
- L5: EHL
- S1: ankle plantarflexion
Sensory
- L2: medial thigh
- L3: medial femoral condyle
- L4: medial mal
- L5: dorsomedial foot
- S1: plantar foot
Digital rectal exam
Assessment of perianal sensation (S3-S4)
Assessment of anal sphinicter tone and strength of sphincter contraction
Provocative maneuvers or special tests
Straight leg raise
Lie flat, raise leg, shooting pain below knee reproduced by elevation > 60 degrees
Hoffman
Hold hand in relaxed position, hold patient’s long finger extended with your thumb and index fingers, flick patient’s distal phalanx of the long finger with your thumb. Positive if patient’s index finger and thumb flex
Clonus
Hold foot in relaxed position, distract patient and rapidly dorsiflex ankle (be gentle). Positive if foot dorsiflexes/plantarflexes in response. Record number of beats.
Bulbocavernous reflex test
To assess if the patient is in spinal shock
With finger inserted into the rectum, squeeze glans penis or clitoris and assess for sphincter contraction
Can also pull traction on foley catheter to stimulate reflex
Spurling Test
Passively have patient rotate head to affected side with slight extension
Positive if upper extremity radicular symptoms occur
Can add axial compression for increased diagnostic sensitivity
L’hermitte Phenomenon
Radicular pain or paresthesia with cervical flexion
Can be an indicator of cervical stenosis and myelopathy